| 导读 | 对于深拷贝的实现,可能存在很多不同的实现方式,关键在于理解其原理,并能够记住一种最容易理解和实现的方式,面对类似的问题才能做到 临危不乱,泰然自若。 |
深度克隆(深拷贝)一直都是初、中级前端面试中经常被问到的题目,网上介绍的实现方式也都各有千秋,大体可以概括为三种方式:
前两种比较常见也比较基础,所以我们今天主要讨论的是第三种。

深拷贝自然是相对浅拷贝 而言的。我们都知道引用数据类型 变量存储的是数据的引用,就是一个指向内存空间的指针, 所以如果我们像赋值简单数据类型那样的方式赋值的话,其实只能复制一个指针引用,并没有实现真正的数据克隆。
通过这个例子很容易就能理解:
const obj1 = {
name: 'superman'
}
const obj2 = obj1;
obj1.name = '前端切图仔';
console.log(obj2.name); // 前端切图仔
所以深度克隆就是为了解决引用数据类型不能被通过赋值的方式 复制 的问题。
我们不妨来罗列一下引用数据类型都有哪些:
ES6之前:对象, 数组, 日期, 正则表达式, 错误,
ES6之后:Map, Set, WeakMap, WeakSet,
所以,我们要深度克隆,就需要对数据进行遍历并根据类型采取相应的克隆方式。当然因为数据会存在多层嵌套的情况,采用递归是不错的选择。
function deepClone(obj) {
let res = {};
// 类型判断的通用方法
function getType(obj) {
return Object.prototype.toString.call(obj).replaceAll(new RegExp(/\[|\]|object /g), "");
}
const type = getType(obj);
const reference = ["Set", "WeakSet", "Map", "WeakMap", "RegExp", "Date", "Error"];
if (type === "Object") {
for (const key in obj) {
if (Object.hasOwnProperty.call(obj, key)) {
res[key] = deepClone(obj[key]);
}
}
} else if (type === "Array") {
console.log('array obj', obj);
obj.forEach((e, i) => {
res[i] = deepClone(e);
});
}
else if (type === "Date") {
res = new Date(obj);
} else if (type === "RegExp") {
res = new RegExp(obj);
} else if (type === "Map") {
res = new Map(obj);
} else if (type === "Set") {
res = new Set(obj);
} else if (type === "WeakMap") {
res = new WeakMap(obj);
} else if (type === "WeakSet") {
res = new WeakSet(obj);
}else if (type === "Error") {
res = new Error(obj);
}
else {
res = obj;
}
return res;
}
其实这就是我们最前面提到的第二种方式,很傻对不对,明眼人一眼就能看出来有很多冗余代码可以合并。
我们先进行最基本的优化:
将一眼就能看出来冗余的代码合并下。
function deepClone(obj) {
let res = null;
// 类型判断的通用方法
function getType(obj) {
return Object.prototype.toString.call(obj).replaceAll(new RegExp(/\[|\]|object /g), "");
}
const type = getType(obj);
const reference = ["Set", "WeakSet", "Map", "WeakMap", "RegExp", "Date", "Error"];
if (type === "Object") {
res = {};
for (const key in obj) {
if (Object.hasOwnProperty.call(obj, key)) {
res[key] = deepClone(obj[key]);
}
}
} else if (type === "Array") {
console.log('array obj', obj);
res = [];
obj.forEach((e, i) => {
res[i] = deepClone(e);
});
}
// 优化此部分冗余判断
// else if (type === "Date") {
// res = new Date(obj);
// } else if (type === "RegExp") {
// res = new RegExp(obj);
// } else if (type === "Map") {
// res = new Map(obj);
// } else if (type === "Set") {
// res = new Set(obj);
// } else if (type === "WeakMap") {
// res = new WeakMap(obj);
// } else if (type === "WeakSet") {
// res = new WeakSet(obj);
// }else if (type === "Error") {
// res = new Error(obj);
//}
else if (reference.includes(type)) {
res = new obj.constructor(obj);
} else {
res = obj;
}
return res;
}
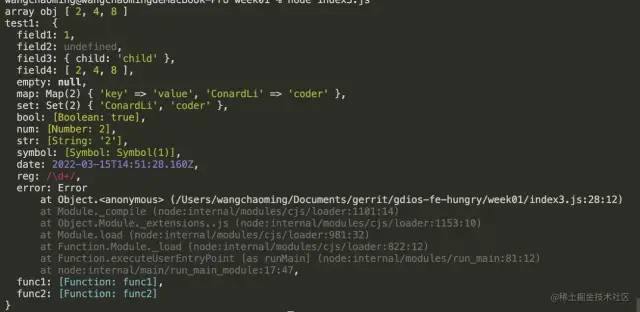
为了验证代码的正确性,我们用下面这个数据验证下:
const map = new Map();
map.set("key", "value");
map.set("ConardLi", "coder");
const set = new Set();
set.add("ConardLi");
set.add("coder");
const target = {
field1: 1,
field2: undefined,
field3: {
child: "child",
},
field4: [2, 4, 8],
empty: null,
map,
set,
bool: new Boolean(true),
num: new Number(2),
str: new String(2),
symbol: Object(Symbol(1)),
date: new Date(),
reg: /\d+/,
error: new Error(),
func1: () => {
let t = 0;
console.log("coder", t++);
},
func2: function (a, b) {
return a + b;
},
};
//测试代码
const test1 = deepClone(target);
target.field4.push(9);
console.log('test1: ', test1);
执行结果:
答案当然是肯定的。
// 判断类型的方法移到外部,避免递归过程中多次执行
const judgeType = origin => {
return Object.prototype.toString.call(origin).replaceAll(new RegExp(/\[|\]|object /g), "");
};
const reference = ["Set", "WeakSet", "Map", "WeakMap", "RegExp", "Date", "Error"];
function deepClone(obj) {
// 定义新的对象,最后返回
//通过 obj 的原型创建对象
const cloneObj = Object.create(Object.getPrototypeOf(obj), Object.getOwnPropertyDescriptors(obj));
// 遍历对象,克隆属性
for (let key of Reflect.ownKeys(obj)) {
const val = obj[key];
const type = judgeType(val);
if (reference.includes(type)) {
newObj[key] = new val.constructor(val);
} else if (typeof val === "object" && val !== null) {
// 递归克隆
newObj[key] = deepClone(val);
} else {
// 基本数据类型和function
newObj[key] = val;
}
}
return newObj;
}
执行结果如下:
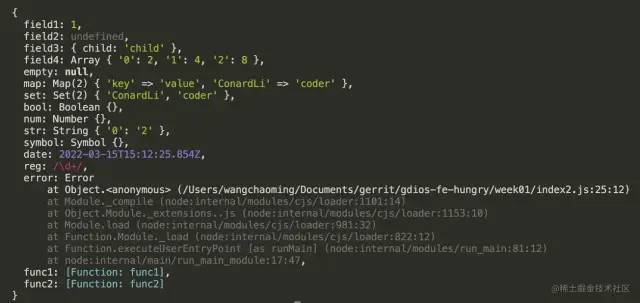
这样做的好处就是能够提前定义好最后返回的数据类型。
这个实现参考了网上一位大佬的实现方式,个人觉得理解成本有点高,而且对数组类型的处理也不是特别优雅, 返回类数组。
我在我上面代码的基础上进行了改造,改造后的代码如下:
function deepClone(obj) {
let res = null;
const reference = [Date, RegExp, Set, WeakSet, Map, WeakMap, Error];
if (reference.includes(obj?.constructor)) {
res = new obj.constructor(obj);
} else if (Array.isArray(obj)) {
res = [];
obj.forEach((e, i) => {
res[i] = deepClone(e);
});
} else if (typeof obj === "Object" && obj !== null) {
res = {};
for (const key in obj) {
if (Object.hasOwnProperty.call(obj, key)) {
res[key] = deepClone(obj[key]);
}
}
} else {
res = obj;
}
return res;
}
虽然代码量上没有什么优势,但是整体的理解成本和你清晰度上我觉得会更好一点。那么你觉得呢?
最后,还有循环引用问题,避免出现无线循环的问题。
我们用hash来存储已经加载过的对象,如果已经存在的对象,就直接返回。
function deepClone(obj, hash = new WeakMap()) {
if (hash.has(obj)) {
return obj;
}
let res = null;
const reference = [Date, RegExp, Set, WeakSet, Map, WeakMap, Error];
if (reference.includes(obj?.constructor)) {
res = new obj.constructor(obj);
} else if (Array.isArray(obj)) {
res = [];
obj.forEach((e, i) => {
res[i] = deepClone(e);
});
} else if (typeof obj === "Object" && obj !== null) {
res = {};
for (const key in obj) {
if (Object.hasOwnProperty.call(obj, key)) {
res[key] = deepClone(obj[key]);
}
}
} else {
res = obj;
}
hash.set(obj, res);
return res;
}
对于深拷贝的实现,可能存在很多不同的实现方式,关键在于理解其原理,并能够记住一种最容易理解和实现的方式,面对类似的问题才能做到 临危不乱,泰然自若。
原文来自:https://juejin.cn/post/7075351322014253064
本文地址:https://www.linuxprobe.com/implementing-deep-copy-requires-least-a-few-lines-code.html编辑:J+1,审核员:逄增宝
Linux命令大全:https://www.linuxcool.com/
Linux系统大全:https://www.linuxdown.com/
红帽认证RHCE考试心得:https://www.rhce.net/