| 导读 | MariaDB Master-Master 复制服务器,可提高速度并减少延迟。使用replication功能,两个独立的 MySQL 服务器充当一个集群。服务器相互同步,以便在发生故障时,其他服务器可以接管并且不会丢失数据。 |
OS:CentOS 8.5
MariaDB: MariaDB 10.3.28
两台主机名称如下:
- Hostname: MasterA ,IP:192.168.232.130
- Hostname: MasterB ,IP:192.168.232.131
使用下面命令在两天服务器中安装mariadb服务:
# MasterA中安装: [root@MasterA ~]# yum -y install mariadb mariadb-server # MasterB中安装: [root@MasterB ~]# yum -y install mariadb mariadb-server
启动mariadb服务:
[root@MasterA ~]# systemctl enable mariadb --now [root@MasterB ~]# systemctl enable mariadb --now
![]()
编辑/etc/my.cnf.d/mariadb-server.cnf配置文件
修改MasterA节点的mariadb-server.cnf配置文件:
[root@MasterA my.cnf.d]# vim mariadb-server.cnf
在mysqld部分下面添加server-id,log-bin 和 log-basename
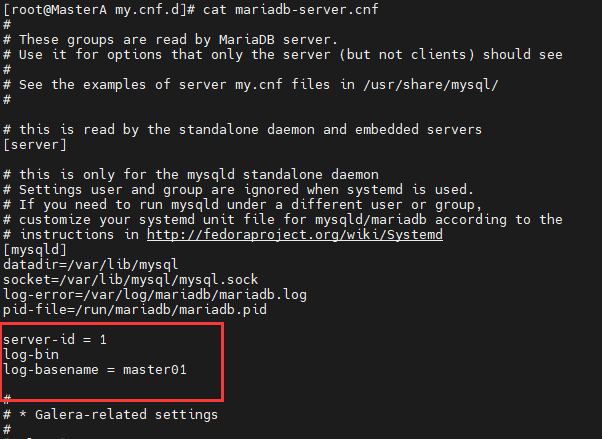
保存配置,并重启MasterA的MariaDB服务。
[root@MasterA ~]# systemctl restart mariadb
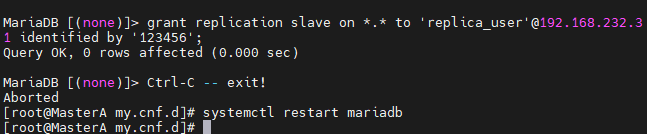
在MasterA的数据库中创建一个帐户,用户名为replica_user,密码为123456,指定slave的IP地址为192.168.232.131,也就是MasterB的IP地址。
MariaDB [(none)]> grant replication slave on *.* to 'replica_user'@192.168.232.131 identified by '123456'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.000 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> flush privileges; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.001 sec)
修改MasterB节点的mariadb-server.cnf配置文件:
[root@MasterB ~]# vim /etc/my.cnf.d/mariadb-server.cnf
在mysqld部分下面添加server-id,log-bin 和 log-basename
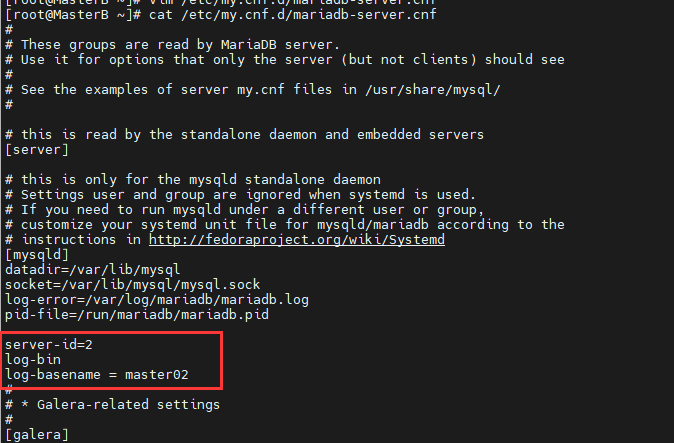
保存配置,并重启MasterA的MariaDB服务。
[root@MasterA ~]# systemctl restart mariadb
在MasterB的数据库中创建一个帐户,用户名为replica_user,密码为123456,指定slave的IP地址为192.168.232.130,也就是MasterA的IP地址。
MariaDB [(none)]> grant replication slave on *.* to 'replica_user'@192.168.232.130 identified by '123456'; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.000 sec) MariaDB [(none)]> flush privileges; Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.001 sec)
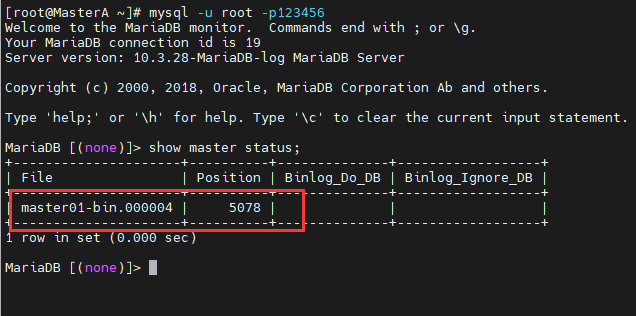
首先进入MasterA操作系统,进入数据库,使用show master status;查看二进制日志名称和pos值:
[root@MasterA ~]# mysql -u root -p123456 Welcome to the MariaDB monitor. Commands end with ; or \g. Your MariaDB connection id is 19 Server version: 10.3.28-MariaDB-log MariaDB Server Copyright (c) 2000, 2018, Oracle, MariaDB Corporation Ab and others. Type 'help;' or '\h' for help. Type '\c' to clear the current input statement. MariaDB [(none)]> show master status; +---------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ | File | Position | Binlog_Do_DB | Binlog_Ignore_DB | +---------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ | master01-bin.000004 | 5078 | | | +---------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ 1 row in set (0.000 sec) MariaDB [(none)]>
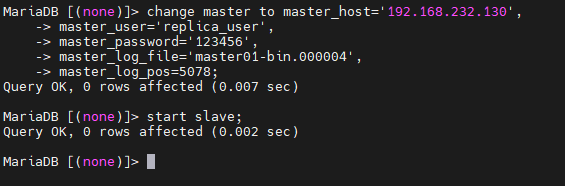
在MasterB系统中进入数据库,指定MasterA服务器的信息,并指定刚才从MasterA获取的bin-log文件名和position值,并启动slave:
MariaDB [(none)]> change master to master_host='192.168.232.130',
-> master_user='replica_user',
-> master_password='123456',
-> master_log_file='master01-bin.000004',
-> master_log_pos=5078;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.007 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]> start slave;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.002 sec)
查看slave状态是否有报错:
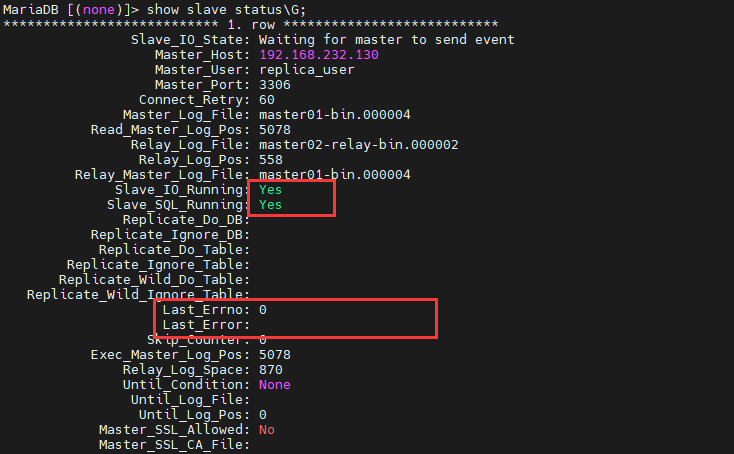
看到上图中,Slave_IO_Running和Slave_SQL_Running都为yes,Last_Error没有错误信息。
其次,在MasterB的数据库中查询master相关信息:
MariaDB [(none)]> show master status; +---------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ | File | Position | Binlog_Do_DB | Binlog_Ignore_DB | +---------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ | master02-bin.000001 | 1080 | | | +---------------------+----------+--------------+------------------+ 1 row in set (0.000 sec)
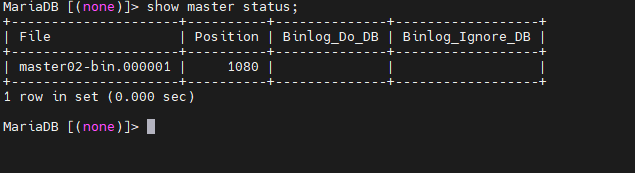
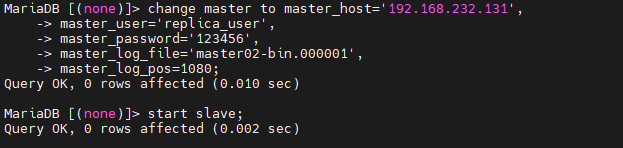
在MasterA系统中进入数据库,指定MasterB服务器的信息,并指定刚才从MasterB获取的bin-log文件名和position值,并启动slave:
MariaDB [(none)]> change master to master_host='192.168.232.131',
-> master_user='replica_user',
-> master_password='123456',
-> master_log_file='master02-bin.000001',
-> master_log_pos=1080;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.010 sec)
MariaDB [(none)]> start slave;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.002 sec)
查看slave状态是否有报错:
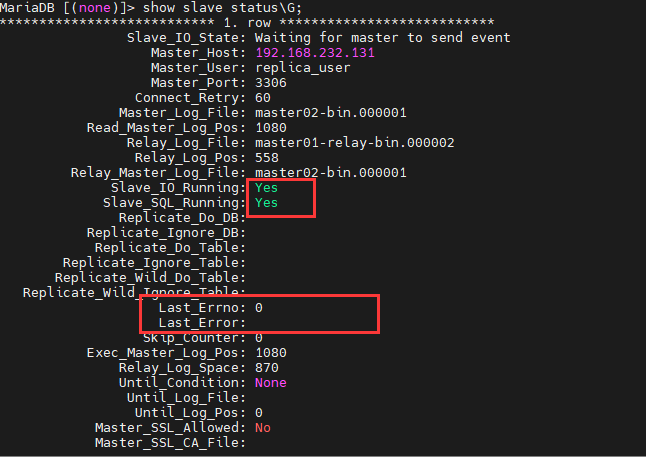
看到上图中,Slave_IO_Running和Slave_SQL_Running都为yes,Last_Error没有错误信息。
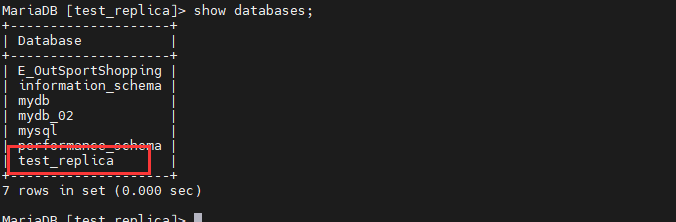
任意一台数据库,创建数据库后,另一台也可以看到了。下面实在MasterB中创建的数据库:
MariaDB [test_replica]> create database mydb; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.000 sec)
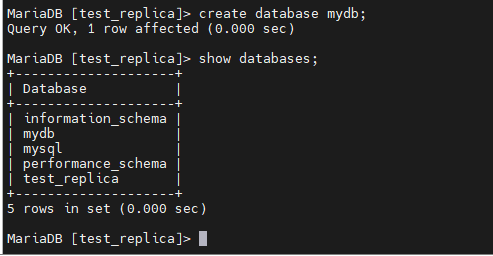
在MasterA中查看是否有mydb数据库:
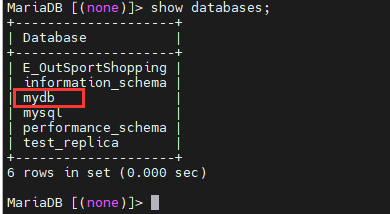
下面是在MasterA中创建数据库:
MariaDB [(none)]> create database mydb_02; Query OK, 1 row affected (0.000 sec)
在MasterB中查看是否有mydb_02数据库:
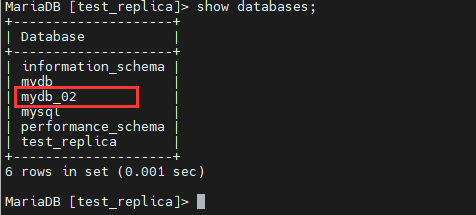
下面实例将MasterA数据库中的test_replica库备份,并导入到MasterB的数据库中,然后在MasterB中的数据库中添加数据,查看是否会同步:
[root@MasterA ~]# mysqldump -u root -p123456 test_replica > a.sql [root@MasterA ~]# scp a.sql root@192.168.232.131:~
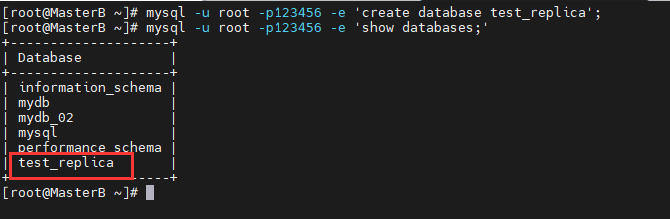
切换到MasterB操作系统,创建一个数据库名称为test_replica:
[root@MasterB ~]# mysql -u root -p123456 -e 'create database test_replica;' [root@MasterB ~]# mysql -u root -p123456 -e 'show databases;'
将MasterA到处的数据导入到MasterB系统中的test_replica库中:
[root@MasterB ~]# mysql -u root -p123456 test_replica < a.sql
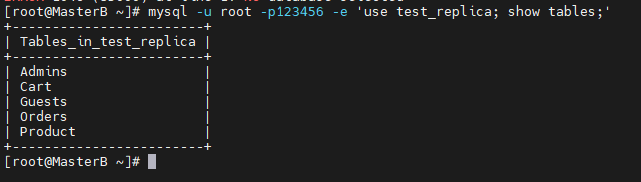
看到已经导入了数据表。
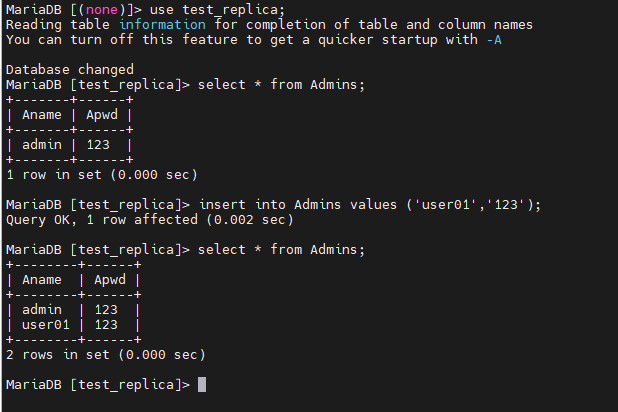
下面在MasterB中,进入test_replica库,向Admins表添加数据,然后在MasterA中查看是否也存在同样数据:
MariaDB [test_replica]> insert into Admins values ('user01','123');
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.002 sec)
在MasterA中查看test_replica数据库中的Admins表:
[root@MasterA ~]# mysql -u root -p123456 -e 'select * from test_replica.Admins;' +--------+------+ | Aname | Apwd | +--------+------+ | admin | 123 | | user01 | 123 | +--------+------+
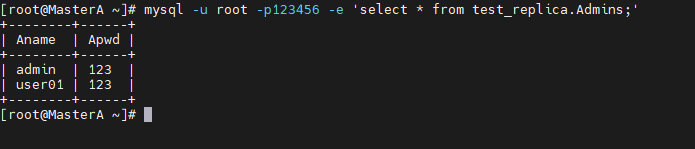
可以看到数据存在。下面在MasterA中向Admins表添加数据,查看MasterB数据库中是否会同步:
MariaDB [test_replica]> insert into Admins values ('user02','321') ;
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.002 sec)

在MasterB中也可以看到刚刚创建的信息:
[root@MasterB ~]# mysql -u root -p123456 -e 'select * from test_replica.Admins;' +--------+------+ | Aname | Apwd | +--------+------+ | admin | 123 | | user01 | 123 | | user02 | 321 | +--------+------+

这样就完成啦。
本文原创地址:https://www.linuxprobe.com/mariadb-master-master-replication.html编辑:逄增宝,审核员:逄增宝