对于 Secure Shell (SSH)[1] 这样的网络协议来说,其主要职责就是在终端模式下访问一个远程系统。因为 SSH 协议对传输数据进行了加密,所以通过它在远端系统执行命令是安全的。此外,我们还可以在这种加密后的连接上通过创建隧道(端口转发)的方式,来实现两个不同终端间的互联。凭借这种方式,只要我们能通过 SSH 创建连接,就可以绕开防火墙或者端口禁用的限制。
这个话题在网络领域有大量的应用和讨论:
- Wikipedia: SSH Tunneling[2]
- O’Reilly: Using SSH Tunneling[3]
- Ssh.com: Tunneling Explained[4]
- Ssh.com: Port Forwarding[5]
- SecurityFocus: SSH Port Forwarding[6]
- Red Hat Magazine: SSH Port Forwarding[7]
我们在接下来的内容中并不讨论端口转发的细节,而是准备介绍一个如何使用 OpenSSH[8] 来完成 TCP 端口转发的速查表,其中包含了八种常见的场景。有些 SSH 客户端,比如 PuTTY[9],也允许通过界面配置的方式来实现端口转发。而我们着重关注的是通过 OpenSSH 来实现的的方式。
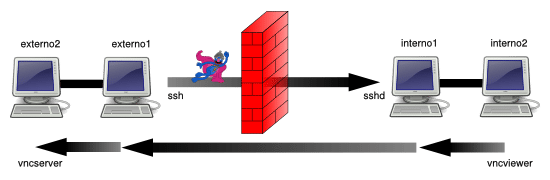
在下面的例子当中,我们假设环境中的网络划分为外部网络(network1)和内部网络(network2)两部分,并且这两个网络之间,只能在 externo1 与 interno1 之间通过 SSH 连接的方式来互相访问。外部网络的节点之间和内部网络的节点之间是完全联通的。
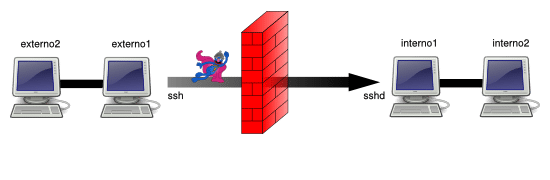
在 externo1 节点访问由 interno1 节点提供的 TCP 服务(本地端口转发 / 绑定地址 = localhost / 主机 = localhost )
externo1 节点可以通过 OpenSSH 连接到 interno1 节点,之后我们想通过其访问运行在 5900 端口上的 VNC 服务。
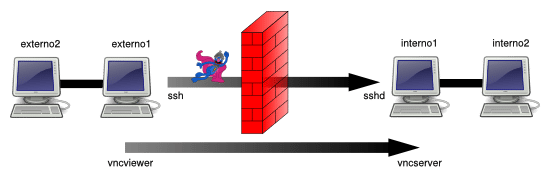
我们可以通过下面的命令来实现:
externo1 $ ssh -L 7900:localhost:5900 user@interno1
现在,我们可以在 externo1 节点上确认下 7900 端口是否处于监听状态中:
externo1 $ netstat -ltn Active Internet connections (only servers) Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State ... Tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:7900 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN ...
我们只需要在 externo1 节点上执行如下命令即可访问 internal 节点的 VNC 服务:
externo1 $ vncviewer localhost::7900
注意:在 vncviewer 的 man 手册[10]中并未提及这种修改端口号的方式。在 About VNCViewer configuration of the output TCP port[11] 中可以看到。这也是 the TightVNC vncviewer[12] 所介绍的的。
在 externo2 节点上访问由 interno1 节点提供的 TCP 服务(本地端口转发 / 绑定地址 = 0.0.0.0 / 主机 = localhost)
这次的场景跟方案 1 的场景的类似,但是我们这次想从 externo2 节点来连接到 interno1 上的 VNC 服务:
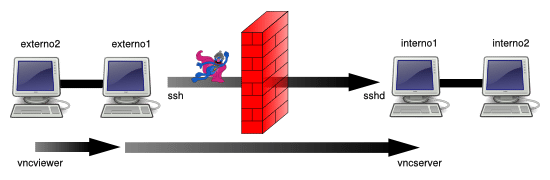
正确的命令如下:
externo1 $ ssh -L 0.0.0.0:7900:localhost:5900 user@interno1
看起来跟方案 1 中的命令类似,但是让我们看看 netstat 命令的输出上的区别。7900 端口被绑定到了本地(127.0.0.1),所以只有本地进程可以访问。这次我们将端口关联到了 0.0.0.0,所以系统允许任何 IP 地址的机器访问 7900 这个端口。
externo1 $ netstat -ltn Active Internet connections (only servers) Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State ... Tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:7900 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN ...
所以现在在 externo2 节点上,我们可以执行:
externo2 $ vncviewer externo1::7900
来连接到 interno1 节点上的 VNC 服务。
除了将 IP 指定为 0.0.0.0 之外,我们还可以使用参数 -g(允许远程机器使用本地端口转发),完整命令如下:
externo1 $ ssh -g -L 7900:localhost:5900 user@interno1
这条命令与前面的命令能实现相同效果:
externo1 $ ssh -L 0.0.0.0:7900:localhost:5900 user@interno1
换句话说,如果我们想限制只能连接到系统上的某个 IP,可以像下面这样定义:
externo1 $ ssh -L 192.168.24.80:7900:localhost:5900 user@interno1 externo1 $ netstat -ltn Active Internet connections (only servers) Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State ... Tcp 0 0 192.168.24.80:7900 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN ...
在 interno1 上访问由 externo1 提供的 TCP 服务(远程端口转发 / 绑定地址 = localhost / 主机 = localhost)
在场景 1 中 SSH 服务器与 TCP 服务(VNC)提供者在同一个节点上。现在我们想在 SSH 客户端所在的节点上,提供一个 TCP 服务(VNC)供 SSH 服务端来访问:
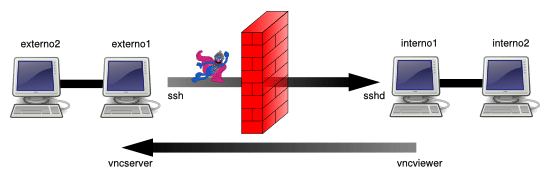
将方案 1 中的命令参数由 -L 替换为 -R。
完整命令如下:
externo1 $ ssh -R 7900:localhost:5900 user@interno1
然后我们就能看到 interno1 节点上对 7900 端口正在监听:
interno1 $ netstat -lnt Active Internet connections (only servers) Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State ... Tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:7900 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN ...
现在在 interno1 节点上,我们可以使用如下命令来访问 externo1 上的 VNC 服务:
interno1 $ vncviewer localhost::7900
interno2 使用 externo1 上提供的 TCP 服务(远端端口转发 / 绑定地址 = 0.0.0.0 / 主机 = localhost)
与场景 3 类似,但是现在我们尝试指定允许访问转发端口的 IP(就像场景 2 中做的一样)为 0.0.0.0,这样其他节点也可以访问 VNC 服务:

正确的命令是:
externo1 $ ssh -R 0.0.0.0:7900:localhost:5900 user@interno1
但是这里有个重点需要了解,出于安全的原因,如果我们直接执行该命令的话可能不会生效,因为我们需要修改 SSH 服务端的一个参数值 GatewayPorts,它的默认值是:no。
GatewayPorts
该参数指定了远程主机是否允许客户端访问转发端口。默认情况下,sshd(8) 只允许本机进程访问转发端口。这是为了阻止其他主机连接到该转发端口。GatewayPorts 参数可用于让 sshd 允许远程转发端口绑定到非回环地址上,从而可以让远程主机访问。当参数值设置为 “no” 的时候只有本机可以访问转发端口;“yes” 则表示允许远程转发端口绑定到通配地址上;或者设置为 “clientspecified” 则表示由客户端来选择哪些主机地址允许访问转发端口。默认值是 “no”。
如果我们没有修改服务器配置的权限,我们将不能使用该方案来进行端口转发。这是因为如果没有其他的限制,用户可以开启一个端口(> 1024)来监听来自外部的请求并转发到 localhost:7900。
参照这个案例:netcat[13] ( Debian # 310431: sshd_config should warn about the GatewayPorts workaround.[14] )
所以我们修改 /etc/ssh/sshd_config,添加如下内容:
GatewayPorts clientspecified
然后,我们使用如下命令来重载修改后的配置文件(在 Debian 和 Ubuntu 上)。
sudo /etc/init.d/ssh reload
我们确认一下现在 interno1 节点上存在 7900 端口的监听程序,监听来自不同 IP 的请求:
interno1 $ netstat -ltn Active Internet connections (only servers) Proto Recv-Q Send-Q Local Address Foreign Address State ... Tcp 0 0 0.0.0.0:7900 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN ...
然后我们就可以在 interno2 节点上使用 VNC 服务了:
interno2 $ internal vncviewer1::7900
在 externo1 上使用由 interno2 提供的 TCP 服务(本地端口转发 / 绑定地址 localhost / 主机 = interno2 )
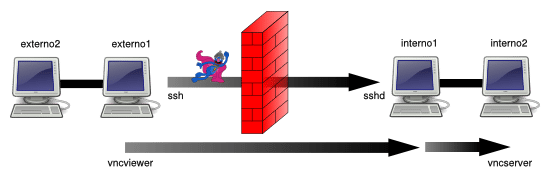
在这种场景下我们使用如下命令:
externo1 $ ssh -L 7900:interno2:5900 user@interno1
然后我们就能在 externo1 节点上,通过执行如下命令来使用 VNC 服务了:
externo1 $ vncviewer localhost::7900
在 interno1 上使用由 externo2 提供的 TCP 服务(远程端口转发 / 绑定地址 = localhost / host = externo2)
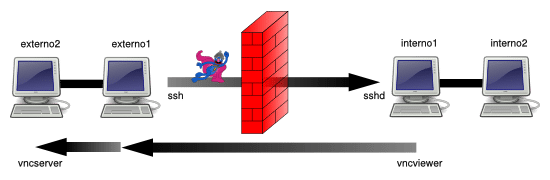
在这种场景下,我们使用如下命令:
externo1 $ ssh -R 7900:externo2:5900 user@interno1
然后我们可以在 interno1 上通过执行如下命令来访问 VNC 服务:
interno1 $ vncviewer localhost::7900
在 externo2 上使用由 interno2 提供的 TCP 服务(本地端口转发 / 绑定地址 = 0.0.0.0 / 主机 = interno2)
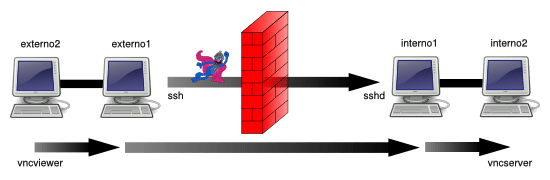
本场景下,我们使用如下命令:
externo1 $ ssh -L 0.0.0.0:7900:interno2:5900 user@interno1
或者:
externo1 $ ssh -g -L 7900:interno2:5900 user@interno1
然后我们就可以在 externo2 上执行如下命令来访问 vnc 服务:
externo2 $ vncviewer externo1::7900
在 interno2 上使用由 externo2 提供的 TCP 服务(远程端口转发 / 绑定地址 = 0.0.0.0 / 主机 = externo2)
本场景下我们使用如下命令:
externo1 $ ssh -R 0.0.0.0:7900:externo2:5900 user@interno1
SSH 服务器需要配置为:
GatewayPorts clientspecified
就像我们在场景 4 中讲过的那样。
然后我们可以在 interno2 节点上执行如下命令来访问 VNC 服务:
interno2 $ internal vncviewer1::7900
如果我们需要一次性的创建多个隧道,使用配置文件的方式替代一个可能很长的命令是一个更好的选择。假设我们只能通过 SSH 的方式访问某个特定网络,同时又需要创建多个隧道来访问该网络内不同服务器上的服务,比如 VNC 或者 远程桌面[15]。此时只需要创建一个如下的配置文件 $HOME/redirects 即可(在 SOCKS 服务器 上)。
# SOCKS server DynamicForward 1080 # SSH redirects LocalForward 2221 serverlinux1: 22 LocalForward 2222 serverlinux2: 22 LocalForward 2223 172.16.23.45:22 LocalForward 2224 172.16.23.48:22 # RDP redirects for Windows systems LocalForward 3391 serverwindows1: 3389 LocalForward 3392 serverwindows2: 3389 # VNC redirects for systems with "vncserver" LocalForward 5902 serverlinux1: 5901 LocalForward 5903 172.16.23.45:5901
然后我们只需要执行如下命令:
externo1 $ ssh -F $HOME/redirects user@interno1
作者:Ahmad[16] 译者:toutoudnf[17] 校对:wxy[18]
本文由 LCTT[19] 原创编译,Linux中国[20] 荣誉推出
原文来自:https://linux.cn/article-8945-1.html
本文地址:https://www.linuxprobe.com/ssh-port-forward.html编辑:逄增宝,审核员:刘遄
本文原创地址:https://www.linuxprobe.com/ssh-port-forward.html编辑:逄增宝,审核员:暂无